A no-effort wellness experience that supports the nervous system during periods of stress
Sound Therapy
What is Sound Therapy
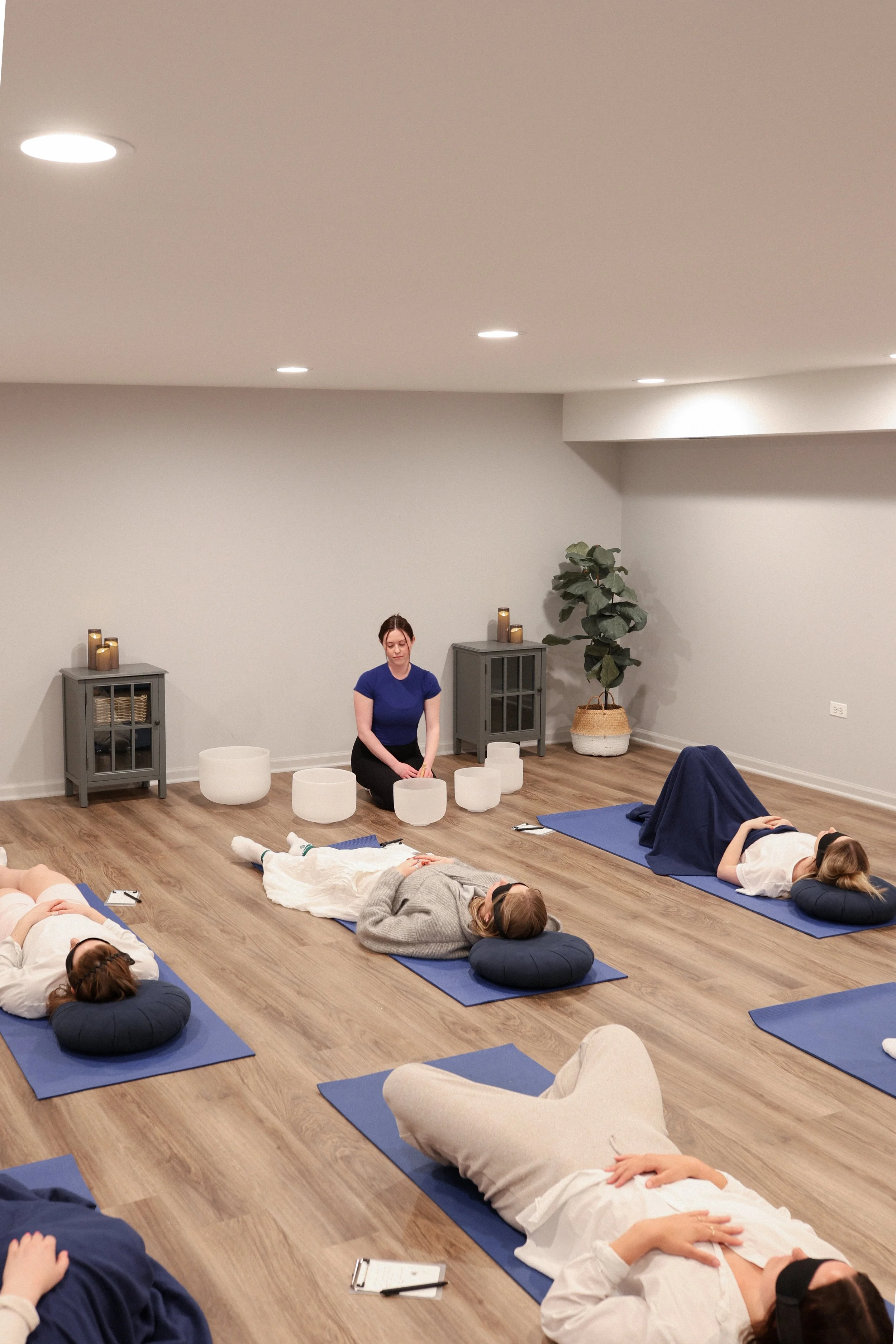
A non-invasive, immersive experience using structured sound to support relaxation and regulation. Participants simply rest and receive while sound is delivered around them.
Sound Therapy Provides Relief & Support
Support for the body - sleep disruption, tension, and nervous system strain associated with chronic illness or medical treatment (such as chemotherapy or radiation)
Improved breathing patterns
Improved sleep quality
Reduced pain sensitivity
Greater access to a calmer internal state
Support for sustained mental load and overstimulation - persistent worry, rumination, overthinking, screen fatigue, stress-related low mood, mental fatigue, and feeling mentally “on”
Clearer thinking and reduced “brain fog”
Easier transition out of work
Greater ease in focus and decision-making
Greater awareness of stress-induced impulses
Deeper sense of presence
What to Expect:
Duration: 60 mins
Simply rest comfortably while sounds fill the room.
Find a comfortable position to rest on a mat.
Rest with eyes open or closed.
Sessions conclude with a gentle grounding transition back to the present moment, similar to the closing of a yoga practice.
Sound therapy works by creating the right vibrational and sensory conditions to support the nervous system’s natural process of downregulation
Vibration
The repeated movement of sound waves. The body responds to these rhythms through sensory and nervous system pathways, shaping internal experience
Each vibration repeats at a measurable rate called frequency.
Frequency
How fast a vibration repeats, which determines perceived pitch.
Sound waves also vary in amplitude or intensity, which shapes how strongly the vibration is experienced.
Amplitude
The intensity or strength of a vibration - often experienced as changes in volume or perceived loudness.
Gradual increases and decreases in amplitude influence how sensory input is received, which may support smoother shifts in nervous system state and set the conditions for resonance to potentially occur.
Resonance
Resonance occurs when one vibrating system influences another with similar properties — allowing energy to transfer and causing the second system to begin vibrating more strongly.
In sound-based practices, the idea that externally generated acoustic waves may interact with biological tissues through similar alignment remains theoretical and is not yet understood in human research.
Sound therapy meets the nervous system exactly where it is, providing whatever support is needed most in that moment.